Announcements of commercial launches
Global 5G race is heating up. The number of live 5G networks increased significantly in Europe and outside Europe since the beginning of 2019. Only Lithuania, Malta and Portugal have not launched 5G services in the EU as at the end of March 2021.
1. Europe
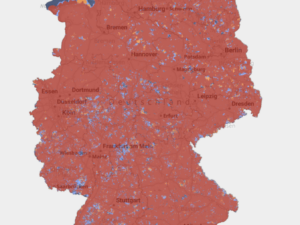
At the end of March 2021, 5G commercial services had been deployed in 24 EU-27 countries: Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Estonia, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Luxembourg, Netherlands, Poland, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain and Sweden.
EU-27 countries with 5G commercial service – March 2021
Source: IDATE Digiworld
Austria
T-Mobile
T-Mobile announced in March 2019 commercial launch with friendly customers using the 3.6 GHz band. The operator announced it had deployed 25 base stations for this launch in rural areas. The first 5G smartphones were available at the end of 2019.
The operator announced in July 2020 that its 5G network was active at 600 locations across the country, covering 25% of Austrian homes and businesses. By the end of 2020, the player reached 1,200 locations, representing almost 40% of homes and businesses. The company noted that it is implementing Dynamic Spectrum Sharing technology.
In September 2020, T-Mobile Austria paid 87 million EUR for 2×20 MHz of 700 MHz spectrum, 20 MHz in the 1500 MHz band and 2×15 MHz of 2.1 GHz spectrum in the second 5G auction in the country.
Three
Three Austria announced a 5G pre-launch after activating its 5G network in the city of Linz in June 2019. The operator activated, in September 2019, more 5G base stations in Worgl and Vienna and started offering 5G tariffs and devices. In December 2019, the company revealed that around 100 5G locations were going to be live across the country by the end of 2019. The operator has worked with Chinese vendor ZTE in its commercial 5G deployment.
A1 Telekom
A1 launched its 5G network in January 2020 using the 3.5 GHz band. The “A1 5Giganetwork” covers 350 locations across 129 municipalities in Austria. A1 had previously signed a commercial contract with Finnish vendor Nokia for the deployment of its 5G network across the country. The contract includes both Nokia’s 5G radio access and cloud-native 5G core technology.
Belgium
Proximus
Proximus launched Belgium’s first commercial 5G services on April 1, 2020, using spectrum in its existing spectrum holdings (2.1 GHz) and within current EMF norms. Coverage was available in about 30 cities and towns. In June 2020, the operator expanded the network coverage to an additional 26 locations in Flanders, including central areas of Ghent and Antwerp. The network was not deployed in the Brussels region due to its stricter radiation standards. By the end of 2020, the network covered more than 100 sites in 62 cities and municipalities, mainly in Flanders.
Bulgaria
Vivacom
In September 2020, Vivacom launched the first Bulgaria 5G network in all 27 district centers of the country. The operator gave free of charge 30 GB per month to its customers to test the new technology until the end of 2020. Vivacom is using Dynamic Spectrum Sharing (DSS) in the 1800 MHz and 2.1 GHz bands.
A1
A1 Bulgaria switched on its 3.6 GHz 5G network in the capital city of Sofia in November 2020. The operator said that the network supports coverage of Sofia’s main residential and business districts and can deliver 1 Gbps download speeds.
Croatia
Hrvatski Telekom
Hrvatski Telekom (HT) switched on Croatia’s first commercial 5G network in late October 2020 in parts of six major cities: Zagreb, Rijeka, Split, Osijek, Samobor and Sveta Nedelja. At launch, 18% of the Croatian population was covered with the 5G network. In December 2020, the operator announced its 5G network covered one million people in 14 cities, reaching 25% of the country’s population. Customers on selected tariffs and with a 5G-capable device can access 5G services at no extra charge until June 2021.
The Hrvatski Telekom’s 5G network is based on Dynamic Spectrum Sharing (DSS) technology, which enables the current use of existing frequencies for 5G. Hrvatski Telekom has launched on 2100MHz bands while awaiting the upcoming 3.5 GHz auction rescheduled for 2021.
Cyprus
Cytamobile-Vodafone
In February 2021, Cypriot mobile operator Cyta launched 5G services capable of providing speeds of 1 Gbps. The company advertised a population footprint of 70% at launch, with plans to extend the coverage to 98% of the population within twelve months.
Czech Republic
Telefonica
O2 (Telefonica) Czech Republic launched 5G services in July 2020 in selected parts of Prague. The network is also available in the city of Koline. In December 2020, the operator announced its network was available in two more cities: Pilsen and Bilina. O2 plans to cover at least three more cities in early 2021.
Vodafone
Vodafone Czech Republic announced in early October 2020 the launch of its NSA 5G network in the cities of Prague, Brno, Usti nad Labem, Jesenik, and Karlovy Vary, using Dynamic Spectrum Sharing technology. In February 2021, the operator communicated that ist 5G network was available in more than 130 cities and smaller municipalities, covering approximately two million people, more than 20% of the population.
T-Mobile
T-Mobile launched 5G commercial services in November 2020 in the cities of Prague and Brno. The operator said that by the end of 2020, more than a quarter of the population in both cities will be covered by its 5G network, targeting having around 360 base transceiver stations online. In December 2020, TMobile announced its 5G network covered one million people in 14 cities.
Operators count on the coming 5G auction for a truly nationwide expansion of the network.
Denmark
TDC
TDC launched commercial 5G services in the 3.5 GHz band in Copenhagen, Odense, Aarhus and Helsingør in early September 2020. The company claimed that by December 2020, 3,800 base stations had been equipped with Ericsson’s 5G technology throughout Denmark, with a footprint of 90% of the population.
The company is offering two 5G plans: the “Professional” with 30 GB of data allowance costs 399 DKK (54 EUR) per month and the “Premium” with 100 GB of data allowance costs 499 DKK (67 EUR) per month. These two 5G price plans complete 4G cheaper plans with lower data allowances (3 GB at 199 DKK/month or 27 EUR and 10 GB at 299 DKK/month or 40 EUR).
Telenor Denmark
Telenor Denmark activated its 5G network in November 2020 using the 3.5 GHz band, covering around 600,000 potential customers in Copenhagen and Aalborg. Cities of Aarhus and Odense are next in line for rollouts.
Telia Denmark
The operator launched commercial 5G services in November 2020 using the 3.5 GHz band. By January 2021, 30% of the population was covered by its 5G network.
Hi3G Access
Danish mobile network operator Hi3G Access announced the official switch-on of its new 5G network in Copenhagen and Roskilde in mid-December 2020. The operator launched 5G using frequencies in the 700 MHz and 1800 MHz. In March 2021 it is expected that the Danish Energy Agency will hold an auction to award spectrum in the 3.5 GHz band. That additional spectrum and further 5G development will enable speeds of around 1 Gbps, 3 Denmark said. The operator announced that it expects to cover one-third of its network by mid-2021 and to complete its nationwide network by mid- 2022.
Estonia
Telia
Telia Eesti switched on Estonia’s first commercial 5G network in November 2020 in the centres of the country’s three largest cities, Tallinn, Tartu and Pärnu. The network uses Ericsson Spectrum Sharing technology, enabling Telia to utilise its existing frequencies since the government has not yet auctioned off 3.5 GHz licences for 5G.
Finland
Elisa
Elisa reported its 5G network carried a 5G phone call on 27 June 2018 between the Estonian minister of Economy and her Finnish colleague in Finland. Tests performed showed data speeds of 2.2 Gbps. That said, the first 5G licences were made available in the 3.6 GHz band frequencies in autumn 2018. The operator started offering 5G mobile devices and plans in June 2019 in Tampere, Jyväskylä, Turku and Helsinki.
Elisa revealed in June 2020 that its 5G network had been switched on in a total of 30 cities and towns across the country, with more than one million people within its service area. In January 2021, Elisa confirmed that its network covered some two million Finns and about 34% of the population, while 5G subscriptions had risen to close to 200,000 by the end of 2020.
Telia
Telia Finland launched 5G services in seven cities at the end of 2019 using its 3.5 GHz spectrum. The operator also promotes Fixed Wireless Access for homes, besides normal mobile subscriptions. In November 2020, the operator stated that its 5G network was covering 42 cities, reaching approximately 1.4 million people or 25% of the population.
DNA
DNA started selling mobile 5G subscriptions in January 2020 using its 3.5 GHz band, having previously launched its ‘DNA Home 5G’ offering in December 2019. In November 2020, the network was available in 76 municipalities, covering more than 1.5 million people and representing 27% of the population.
France
Orange
Orange France launched its commercial 5G mobile network on 3 December 2020 in 15 municipalities including Nice, Marseille, Le Mans, Angers, and Clermont Ferrand. By the end of 2020, more than 160 municipalities will be covered with the 3.5 GHz 5G network, providing data speeds up to three-to-four times faster than 4G LTE. According to Orange, each municipality will be added to the official coverage list when its 5G outdoor population coverage rate reaches 80% or more.
Bouygues Telecom
Bouygues Telecom switched on its 5G network in 20 major cities the 1st of December 2020. The network was available in Lyon, Nice, Montpellier, Reims, Le Havre, Toulon, Dijon, Villeurbanne, Le Mans, Aix-en-Provence, Boulogne-Billancourt, Metz, Saint-Denis, Argenteuil, Rouen, Versailles, Montreuil, Nancy, Avignon, and Cannes. In January 2021, Bouygues announced its 5G rollout reached over 1,000 municipalities across the country via 2,407 base stations. The French operator has also confirmed the goal of achieving nationwide coverage by the end of 2021. The current roll-out phase will rely on the 3.5 GHz and 2.1 GHz bands.
SFR
SFR announced in late November 2020 the launch of its 5G service using the 2.6 GHz and 3.5 GHz in the city of Nice. 50% of the population of the city was covered by 5G, and within several weeks, 80% was planned to be covered. The company confirmed plans to extend its coverage to more than 120 municipalities throughout December 2020. The rollouts will take place at selected locations in the agglomerations of Bordeaux, Marseille-Aix-en-Provence, Montpellier, Nantes, Nice, and Paris-Ile-deFrance.
Free
Free Mobile became in December 2020 the fourth French operator to launch commercial 5G services. At launch, for the same data volume, consumers had to pay more than three times at Orange or at SFR.
The 5G network covered about 40% of the population and had good indoor reception thanks to the 5,255 active 700 MHz cell sites. Free Mobile also activated 220 cell sites equipped with 3.6 GHz frequencies to offer ultra-fast speeds in selected locations. By February 2021, the operator had activated 6,274 base stations.
France’s spectrum agency ANFR said that the number of cell sites authorized for 5G services amounted to 18,039 as of January 7, 2021.
Germany
Deutsche Telekom
Deutsche Telekom switched on its 5G network in September, 2019, in five German cities: Berlin, Bonn, Cologne, Darmstadt, and Munich. Hamburg, Frankfurt, and Leipzig followed.
In July 2020, the operator announced that its 5G network covered 40 million Germans, representing half of the population. Services were available in over 3,000 towns and municipalities after a further 18,000 antennas were upgraded for 5G and integrated into the live network. The company announced that it plans to cover 80% of the population by the end of 2021.
Telekom uses spectrum in the 2.1 GHz band to provide customers with 5G coverage in less densely populated areas, while the 3.6 GHz band is being used in large cities. Dynamic Spectrum Sharing is also being deployed.
Vodafone Germany
Vodafone Germany started its 5G network in July 2019. In February 2021, the operator announced that it switched on a further 2,200 5G antennas at around 800 locations across Germany. In total, more than 7,000 5G antennas were active at almost 2,500 locations, providing coverage to more than 20 million Germans, with this set to rise to 30 million by the end of 2021.
Vodafone is using the 1800 MHz band to provide 5G in densely populated cities with speeds of more than 500 Mbps, while the 700 MHz range is being deployed in rural areas to offer data rates of up to 200 Mbps and the 3500 MHz band is being rolled out in high traffic areas such as stadiums and train stations, where it is able to support speeds of 1 Gbps.
Telefonica
Telefonica became Germany’s third mobile network operator to introduce 5G services in October 2020, when the network was activated in ten cities: Berlin, Hamburg, Munich, Frankfurt, Cologne, Dusseldorf, Stuttgart, Essen and Potsdam. Telefonica’s 5G network in the 3.6 GHz band will have grown from 450 antennas to over 6,000 to cover more than 30% of the population by the end of 2021. The operator expects to reach around 50% by the end of 2022 and the whole country by 2025. In rural areas, the company will use Dynamic Spectrum Sharing.
Greece
Wind Hellas
Greek mobile operator Wind Hellas announced in December 2020 that it switched on its 5G mobile network a few days after winning frequencies in the country’s multi-band 5G spectrum auction. The network was initially covering Athens and Thessaloniki, while coverage of other major cities is expected in 2021. The operator said that 5G population coverage is expected to exceed 60% within three years.
Cosmote
Cosmote launched its commercial 5G services in December 2020 in Athens, Thessaloniki and other Greek cities, with speeds exceeding 1 Gbps in certain areas. In March 2021, the operator expanded its 5G network to cover 17 cities, including 90% of the population of the country’s two largest cities, Athens and Thessaloniki. The company is aiming to increase coverage to over 50% of the population by the end of 2021. Vodafone Greece
In January 2021, Vodafone Greece became the country’s third mobile operator to switch on its 5G network. The services were available in parts of Athens and Thessaloniki, with 40% of the population expected to be covered by March 2022.
Hungary
Vodafone Hungary
In October 2019, Vodafone Hungary launched a commercial 5G service limited to Budapest, using its existing 3.5 GHz spectrum and ahead of Hungary’s March 2020 licence auction where it won additional 3.5 GHz frequencies plus a 700 MHz licence. In March 2021, the operator announced that its 5G network was available ‘in most of Budapest’.
In late June 2020, the operator announced plans to roll out 5G services in six cities, focusing on the busiest parts of inner cities and around universities. The rollouts will increase the number of Vodafone 5G base stations to about 300.
Magyar Telekom
The operator launched commercial 5G mobile network services in April 2020 in partnership with Ericsson. The network was available in limited areas of Budapest and Puskas Ferenc stadium. By September 2020, the network was available in parts 18 cities and towns including Zalaegerszeg, Szombathely, Debrecen, Szeged and Kecskemét.
Ireland
Vodafone
Vodafone Ireland launched 5G services in August 2019 in selected areas of five Irish cities, including Dublin and Waterford using the 3.5 GHz band. In May 2020, the operator communicated that the 5G network was live in Cork, Dublin, Galway, Limerick and Waterford.
Eir
In early December 2019, Eir launched its 5G service in 10 towns and cities using the 3.5 GHz band. By January 2020, 5G services were available in 20 towns and cities. In February 2021, Eir confirmed that its 5G network covered 55% of the population, with infrastructure available in 239 towns and cities via more than 800 base stations.
Three Ireland
In late September 2020, Three Ireland started offering 5G commercial services with Ericsson’s equipment in a total of 315 sites across Ireland, reaching 35% of population coverage using the 3.7 GHz band. The operator expects to add a further 500 5G-capable sites in 2021. Ericsson announced that the 5G network is powered by the vendor’s fully virtualised 5G Core and the latest products and solutions from its Radio System portfolio.
Italy
Vodafone
Vodafone Italy launched its commercial 5G services in 5 cities on 6 June 2019 (Milan, Rome, Turin, Bologna and Naples). In Turin, the Vodafone network covered 80% of the city with 120 cell sites. The number of cities with 5G availability is meant to increase up to 100 by the end of 2021. The operator inked a network sharing 5G deal with Telecom Italia in early 2019.
Telecom Italia
TIM launched its 5G service on June 24th, 2019 in parts of Rome and Turin, Naples followed in July 2019. As of late March 2020, 5G services were available in Bologna, Brescia, Florence, Genoa, Milan, Naples, Turin, and Rome. In August 2020, the network was available in a total of ten cities. The company announced plans to reach 120 cities by the end of 2021.
Windtre
Wind Tre launched its 5G network in around ten regional capitals in October 2020. The operator announced in January 2021 it had rolled out 5G networks in 59 Italian provinces and eight additional provincial capitals, covering around 73.7% of the population.
Iliad Italia
Iliad Italia switched on its 5G network in 27 Italian cities in December 2020. The operator launched what it could be a highly disruptive offer in Italia, a 5G called Flash 70 for under 10 EUR for a limited period only, until January 21, 2021. The operator did not say what the price will be after the offer period.
Latvia
LMT
Latvian Mobile Telephone launched 5G network in July 2019, with limited availability. In January 2020, commercial 5G services were extended to the cities of Jelgava and Daugavpils.
Tele2
Tele2 Latvia commercially launched 5G services in Daugavpils and Jelgava in January 2020. The operator said any customer with a compatible device could use the 5G network. By September 2020, the network was available in Riga, Jurmala, and Valmiera. In January 2021, the operator announced plans to expand its 5G network with the deployment of base stations in 13 more cities over the course of 2021.
Luxembourg
Orange
The operator confirmed the network was activated in November 2020 covering Luxembourg City and surrounding areas, such as Bertrange, Strassen, Kirchberg and the airport. Orange subscribers can access 5G services at no extra charge as part of their existing mobile plans.
Tango
Luxembourg mobile network operator Tango launched 5G services in November 2020. The 5G network was initially available in Luxembourg City before being deployed in other larger towns from early 2021. All customers can benefit from the new 5G network with their current mobile subscription, reaching speeds of up to 1 Gbps.
Netherlands
VodafoneZiggo
The operator activated its 5G network in late April 2020 across more than half of the Netherlands. VodafoneZiggo announced plans to cover all of the Netherlands by late 2020. In partnership with Ericsson, the operator implemented 5G services via its existing antennas and Dynamic Spectrum Sharing technology which allows operators to dynamically allocate some of their existing 4G LTE spectrum to 5G. More specifically, the company is using 800/1800/2100/2600 MHz bands.
The company notes that the mobile data download speeds that 5G can offer using its existing spectrum reach a maximum of 1 Gbps, although it adds that in practice the 5G data rates experienced by initial customers will be on average 10% higher than the 4G speeds (maximum of 350 Mbps) they were previously getting.
T-Mobile
In late July 2020, T-Mobile Netherlands launched its 5G mobile network in The Hague and ‘most of the Netherlands’. The operator confirmed that its initial 5G network is based on its new 700 MHz spectrum, with existing subscribers to its Unlimited and Unlimited Plus subscriptions automatically receiving 5G access on suitable devices. The company announced in January 2021 that it reached 90% 5G population coverage. KPN
KPN launched commercial 5G services the same day as T-Mobile, in late July 2020 using its 700 MHz spectrum band. The network covered over 90% of the top five Dutch cities, Amsterdam, Rotterdam, The Hague, Utrecht,
and Eindhoven, reaching approximately half of the Netherlands’ population. The operator plans to offer nationwide 5G coverage by the end of 2021. KPN announced that B2B customers will be able to purchase special 5G-only services including coverage-on-demand, application priority and guaranteed bandwidth.
Poland
Polkomtel (Plus)
Polish operator launched the country’s first commercial 5G mobile network in May 2020. The network used 100 base stations in the 2.6 GHz band, providing 5G services in seven cities and to about 900 000 people: Warsaw, Gdansk, Katowice, Lodz, Poznan, Szczecin and Wroclaw. Polkomtel communicated there were 5.2 million people covered by its 5G networks at the end of November 2020. The company is planning to have coverage of eleven million Poles in 150 cities and towns with 1,700 base stations by the end of 2021.
Orange Poland
The operator launched 5G services via 1,600 base stations, using the 2.1 GHz band and covering up to six million people in July 2020. T-Mobile aimed to cover by the end of June 2020, Warsaw, Lodz, Krakow, Poznan, Wroclaw, Plock, Opole, Czestochowa, Rzeszow, Bielsko-Biala and Kielce. The network uses the 2.1 GHz band.
Play
The operator announced the launch of its commercial 5G services in June 2020 over 50 base stations in 16 cities using the 2.1 GHz band.
Romania
Vodafone
Vodafone launched 5G services in Romania on 26 June 2019 in areas of three cities. Customers could choose two 5G plans: The Red Infinity 17 with unlimited 5G data at EUR 17 per month and Red Infinity 25 with unlimited 5G data and more services at EUR 25 per month.
Digi
RCS&RDS (Digi) announced its first 5G commercial service in June 2019, in areas of six cities. The company offered two 5G compatible smartphones: the Xiaomi Mi Mix 3 5G and the Huawei Mate 20x 5G.
Orange
In November 2019, Orange Romania launched 5G in Bucharest, Cluj-Napoca and Iasi. The operator announced in January 2020 the expansion of its 5G network to Brasov and Poiana Brasov.
In late August 2020, Orange Romania announced its 5G network in Bucharest had been expanded to cover the entire city, enabling 100% of its population to access download speeds of up to 1.2 Gbps. The network was also expanded to Mamaia and Timisoara.
Slovakia
Slovak Telekom
Slovak Telekom became the country’s first operator to launch commercial 5G services in December 2020. Services were available in eight districts of Bratislava. ST announced that customers can expect download speeds of between 300 Mbps and 600 Mbps, and between 60 Mbps and 80 Mbps for upload. The operator is utilizing 15 MHz of frequencies in the 2.1 GHz band, in combination with LTE spectrum.
Slovenia
Telekom Slovenije
Telekom Slovenije launched the first commercial 5G network in Slovenia in July 2020. The mobile operator upgraded 150 4G base stations to support 5G and announced that it provided coverage to approximately 25% of the population. By the end of 2020, Telekom Slovenije expected to surpass 33% coverage.
Ericsson announced that Telekom Slovenije is using its Radio Access Network (RAN) and Cloud Core solutions for its 5G commercial rollout. Ericsson also assisted with a software installation to existing Ericsson Radio System and packet core equipment, which enables spectrum sharing between 4G and 5G on 2.6 GHz FDD spectrum.
Spain
Vodafone
Vodafone Spain launched its commercial 5G services at 3.7 GHz in 15 cities in June 2019 with initial speeds of up to 1 Gbps. At launch, the service was reaching approximately 50% coverage in each of the 15 cities.
Vodafone Spain activated in June 2020 its 5G network in a total of 21 cities. The company had previously said that it was working with Huawei and Ericsson in the deployment of the 5G network.
Telefonica
Telefonica announced in September 2020 the switched on of its 5G network in unspecified Spanish locations. The network utilises 3.5 GHz spectrum, alongside re-farmed 1800 MHz and 2.1 GHz frequencies. Telefonica announced it awarded Finnish vendor Nokia the contract to increase 5G coverage up to 75% of the Spanish population by year-end 2020. Nokia is the only vendor to supply 5G radio technology to all of Telefonica’s 5G operations across Europe.
Orange
In September 2020, Orange Spain launched 5G mobile services using the 3.5 GHz band in selected parts of five cities, namely: Madrid, Barcelona, Valencia, Seville and Malaga, predominantly in central areas. Orange covered around 30% of each city. The operator announced in March 2021 that its 5G network covered 295 municipalities across 38 provinces, equivalent to population coverage of 23%. The telco expects its 5G service to reach more than 400 cities by the end of 2021, providing coverage of over 51% of the population. In 2022, coverage is expected to reach 90%, via a combination of NSA 5G architecture and Dynamic Spectrum Sharing technology.
The Ericsson Radio System, delivering Massive MIMO, powers the 3.6 GHz 5G network in Madrid and Barcelona. Ericsson also supplies Orange Spain with a 5G Evolved Packet Core to support the 5G New Radio non-standalone 5G network.
MASMOVIL
In September 2020, Grupo MASMOVIL became the fourth Spanish operator to launch 5G services, after switching on connectivity in 15 cities. The carrier said that the 5G service is being offered via a combination of its own infrastructure and an agreement with rival operator Orange.
Sweden
Tele2
Tele2 switched on 5G networks in Stockholm, Gothenburg and Malmo on May 24, using 80 MHz of the 3.6 GHz spectrum band. The operator communicated in November 2020 that it expanded its 5G network to 30 new locations. The firm said that speeds of up to 1 Gbps are available at most 5Genabled locations.
Telia Sweden
Telia Sweden announced in May 2020 that its 5G network was active through 15 base stations in Stockholm, using its existing 700 MHz spectrum, boosted by LTE and New Radio carrier aggregation. In December 2020, the operator announced that its 5G network was available in 20 cities. The company is working with local partner Ericsson, which confirmed it is providing radio access network products and solutions. Certified by the Swedish Society for Nature Conservation, the 5G network is powered by 100 % renewable energy.
Tre
In late June 2020, Tre Sweden announced the commercial launch of 5G services in Malmo, Lund, Uppsala, Helsingborg, Vasteras and large parts of Stockholm. The operator activated 385 5G base stations, 200 of which are in Stockholm, and expected to cover most of the centre of the capital by the end of August.
Telenor
Telenor Sweden launched commercial 5G services in central Stockholm in October 2020, becoming the fourth 5G network in the country. The operator said its network will provide internet access at 1 Gbps to customers with a compatible handset and a Telenor 5G-ready 30 GB, 75 GB, or unlimited subscription. 5G network coverage is available in at least half of the city centre. The operator intends to widen its footprint in the capital while also adding connectivity in Malmo and Gothenburg before expanding the rollout to towns with a population of over 50,000. Telenor also said that it expects its 5G network to cover 99% of Sweden’s population by 2023.
2. Rest of Europe
Norway
Telenor Norge began offering a commercial 5G service in March 2020, becoming the first operator in the country to do so. The 5G network initially available in nine locations across the country: Kongsberg, Elverum, Bodo, Askvoll, Fornebu, Kvitfjell, Spikersuppa, Oslo and Trondheim. In November 2020, Telenor launched an FWA 5G service.
In May 2020, Telia launched 5G for customers in Lillestrøm and parts of Groruddalen in Oslo, with plans to expand to other areas during 2020. In November 2020, Telia launched an FWA 5G service.
Switzerland
In Switzerland, Sunrise announced partial 5G commercial launch in March 2019 and full launch in September 2019. Swisscom launched in April 2019. At launch, Swisscom’s network encompassed 100 sites in 50 cities and villages. The Swiss operator was targeting more than 90 percent population coverage by the end of 2019.
United Kingdom
EE
EE launched 5G services in May 2019 across six cities, including some areas of London, Edinburgh, Cardiff, Belfast, Birmingham, and Manchester. The network had targeted to bring 5G connectivity in 45 cities and large towns by the end of 2019.
As of June 2020, EE’s 5G service was live in 80 towns and cities across the country, announced the UK carrier. The company is using a Non-standalone 5G New Radio deployment focused on using the combined power of 4G and 5G technologies. In a second phase from 2022, it will introduce the full 5G core network, enhanced device chipset capabilities, and increased availability of 5G-ready spectrum. A third phase, beginning in 2023, will introduce Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communications (URLLC), network slicing and multi-gigabit-per-second speeds.
In January 2021, EE announced that it was offering 5G connectivity in a total of 125 towns and cities across the country.
Three UK (FWA)
Three UK launched its 5G network for smartphone users in February 2020 in 65 locations, including parts of London, Cardiff, Glasgow, Manchester, Birmingham, Coventry and Nottingham. The 5G network went live earlier in August 2019. It was available in central London and to Three Broadband service users only.
In March 2021, Three UK issued a network update, revealing that it had 1,250 5G sites in operation across 193 towns and cities, up from around 1,000 at the end of 2020. Further, it expects ‘hundreds of more sites’ to come online before the end of 2021 and notes that its 5G home broadband services now cover 1.6 million premises.
Vodafone
Vodafone launched 5G services in the UK in July 2019 in seven cities. It planned to offer 5G services in twelve additional UK cities by ear-end 2019. Vodafone UK confirmed in July 2020 that its 5G network footprint at that date covered a total of 44 locations, while it also claimed to have ‘massively expanded’ coverage in launch cities.
Telefonica (O2)
Telefonica (O2) became in October 2019, the latest mobile operator to switch on its 5G network in the UK. Services were available in six cities and towns: Cardiff, Belfast, Edinburgh, Leeds, London, and Slough. As of June 2020, the 5G network was live across parts of 60 towns and cities in the country, up from 20 at the start of 2020.
The company revealed in January 2021 that it was offering 5G services in in over 150 towns and cities nationwide. Telefonica also noted that it has increased its 5G coverage footprint ‘significantly’ in bigger cities such as London, Birmingham, Glasgow, Bristol, Liverpool, and Manchester.
3. South Korea
SK Telecom, LGU+ and KT launched 5G services in December 2018 for business customers and in April 2019 for residential users.
MNOs announced in July 2018 their intention to jointly launch 5G in March 2019. This intention arrived one year after a first agreement signed in April 2018 on a shared 5G deployment and network. This first agreement’s intention aimed at avoiding a very costly launch campaign when 4G came to reality back in 2011 and generating heavy cost savings of nearly 1 billion USD over the next ten years.
The Korean government announced that operators had deployed in early 2020 a total of 115,000 5G base stations across the country.
The country ended January 2021 with 12.87 million 5G subscribers, according to data from the Ministry of Science and ICT. South Korean telcos are expecting a big surge in 5G adoption in 2021, according to local press, with top wireless carrier SK Telecom aiming to have 9 million 5G users by the end of 2021, and smaller rival LG Uplus targeting 4 million.
At the end of January 2021, total mobile subscriptions in the Asian nation stood at 70.69 million, with 4G subscriptions at 51.9 million, down 660,000 compared to December 2020. As of early 2021, South Korean telecom operators provide 5G services via NSA 5G networks and are mostly in large cities. The companies are preparing to commercialize new technology, such as Standalone versions of the 5G networks and millimeter-wave 5G.
4. Australia
Telstra Australia
The operator launched its 5G service on the 3.6 GHz band at the end of May 2019 as it had switched on over 200 5G sites since August 2018. The 5G service was available in over 10 cities, twenty-five additional cities were expected to be covered before end-June 2020. The operator announced it was ahead of its target and 5G services were available in 47 cities across the country by summer 2020.
Telstra and Swedish vendor Ericsson announced collaboration agreements to provide 5G equipment and upgrade Telstra’s network.
In September 2020, the operator announced that it had more than 1,500 5G sites in operation across selected areas of 53 cities and towns covering around ten million people.
In January 2021, the Australian operator announced that its 5G network covered 50% of the country’s population and that it plans to increase coverage to 75% before the end of June 2021.
Telstra previously acquired spectrum in the 3.6 GHz auction for AUD 386 million (EUR 240 million), giving it 60 MHz of contiguous 5G spectrum in all major capital cities and between 50 MHz and 80 MHz in regional areas.
Optus
Rival mobile network operator Optus announced the commercial launch of 5G mobile and 5G residential fixed broadband services covering selected areas in November 2019. 290 5G base stations went live in Sydney, Canberra, Adelaide, Brisbane, Melbourne, Perth and other locations in New South Wales, Victoria and Queensland, noting that 1,200 sites were planned by March 2020. The telco failed to achieve that target and announced in January 2021 it had 1,000 active 5G base stations.
Optus is using equipment from both Ericsson and Nokia in its rollout of 5G. The company secured spectrum in the 3.6 GHz spectrum auction for AUD 185 million (EUR 110 million) in late 2018.
Vodafone Australia
The telco switched on, in March 2020, its first 5G sites in Parramatta and confirmed plans to expands its network in Sydney, Melbourne, Brisbane, Adelaide, Canberra and Perth in summer 2020.
5. Japan
NTT DOCOMO
NTT DOCOMO launched Japan’s first 5G smartphone service on March 25, 2020. The network was live in 150 areas in the country covering 29 of Japan’s 47 prefectures. By March 2021, more than 500 cities are expected to have access to the next-generation network. The operator expects to reach 10,000 5G sites by June 2021 and 20,000 by March 2022.
KDDI
KDDI launched 5G mobile services in 15 of Japan’s 47 prefectures on March 26, 2020. The operator said it aimed to install 10,000 base transceiver stations by March 2021 and another 10,000 BTS by the end of March 2022. By 2025, the company plans to cover 93% of the populated areas of the country, as well as install 30,107 base stations in the 3.7 GHz and 4.5 GHz spectrum bands and 12,756 base stations in the 28 GHz band.
SoftBank
SoftBank turned on its 5G network on March 27, 2020. 5G mobile services were available in selected areas in seven prefectures across Japan. The operator aims to install over 10,000 5G base stations by the end of March 2023. By 2025, the company plans to expand its network to roughly 64% of the populated areas of the country and install 7,355 base stations in the 3.7 GHz and 4.5 GHz spectrum bands and 3,855 base stations in the 28 GHz band.
SoftBank and KDDI teamed together to speed up 5G rollout in rural areas. To this end, they announced on April 1st, 2020 the setup of a joint venture, 5G JAPAN. The joint venture’s goal is to promote infrastructure sharing based on the mutual use of base station assets held by the two companies. The initial capital of the joint venture will be 500 million JPY (4.24 million EUR) and each operator will own 50% of the stakes.
Rakuten
Greenfield operator Rakuten launched commercial 5G services in late September 2020 in certain areas across six prefectures of the country. The service initially offered via Non-Stand Alone (NSA) 5G architecture, was available in parts of Tokyo, Kanagawa, Saitama, Hokkaido, Osaka and Hyogo. Rakuten Mobile’s President Yoshihisa Yamada said that the operator is expecting the 5G to be available in Japan’s all 47 prefectures by end-March 2021. Rakuten claims to have launched the world’s first fully virtualized mobile network that uses lower-cost and more up-to-date cloud and software technologies. The operator expects to launch a Stand-Alone 5G network in the second quarter of 2021.
The Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications planned to start allowing certain 4G frequencies to be converted to 5G this summer, which would let providers use existing base stations to power 5G networks.
6. China
In December 2018, China issued test licences to players for national 5G trials until June 2020 (China Telecom: 3.4-3.5 GHz, China Unicom: 3.5-3.6 GHz, 260 MHz on 2515-2675 MHz and 4800-4900 MHz). The country awarded four 5G licences to China Mobile, China Unicom, China Telecom and China Broadcasting Network, earlier in June 2019, faster than anticipated.
China Mobile, China Telecom and China Unicom launched 5G services on November 1st, 2019. Each player activated their network in 50 cities at launch, including Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Hangzhou, Nanjing, Tianjin, Wuhan, Jinan, and Zhengzhou. In early October 2019, the three major mobile operators had already registered almost 9 million 5G users before the official launch. China Mobile announced 5.32 million subscribers, China Telecom hit 1.76 million subs, and China Unicom was right in line with 1.75 million users.
China Mobile announced it ended November 2020 with a total of 147.4 million 5G subscribers, compared to 6.7 million 5G customers in January 2020. Rival operator China Telecom added 7.6 million subscribers in November 2020 to take its total 5G subscribers base to 79.5 million. China Unicom has not revealed its 5G numbers. Not all “5G package subscribers” announced by the players are in possession of a 5G-capable handset. This overstates the actual 5G user numbers.
The Ministry of Industry and Information Technology announced that by April 2020, telecommunications companies had built more than 250,000 5G base stations across the country. By September 2020, the number of base stations built was 500,000.
The tech hub, often referred to as China’s answer to Silicon Valley, was home to about 46,000 5G cell sites as of September 2020.
In early 2021, China Mobile announced it ended the first month of the year with a total of 168.97 million 5G subscribers, compared to 6.7 million 5G customers in January 2020. The carrier have deployed over 385,000 5G base stations nationwide, according to local press reports. Rival operator China Telecom added 10.67 million 5G subscribers in January 2021 to take its total 5G subscribers base to 97.17 million. China Unicom has not revealed its 5G subscribers numbers.
China’s vice-minister of industry and information technology communicated in early 2021 that a total of 718,000 5G base stations were built in China in 2020, accounting for ‘nearly 70% of the world’s total 5G sites’. About 100,000 5G base stations were built in 2019. In 2021, local carriers are expected to deploy approximately 600,000 5G base stations, according to recent reports.
Local operators said that they already provide 5G coverage in all Chinese cities at prefecture level and above. The Chinese government has been encouraging 5G partnerships to boost efficiency and accelerate network rollouts.
In September 2019, China Telecom and China Unicom agreed to share their 5G SA infrastructure. The deal could save about 9 billion EUR in construction investment by preliminary estimate. In May 2020, China Mobile signed a 5G network sharing agreement with China Broadcasting Network, which jointly fund and deploy a network over the 700 MHz frequency.
7. USA
Verizon
Verizon 5G Home service was launched in October 2018 in limited areas of four US cities (Houston, Sacramento, Indianapolis, Los Angeles). The telco noted that the platform can deliver peak speeds of up to 1 Gbps, although users could expect ‘typical’ speeds of around
300 Mbps. In early October 2020, the service was also available in Chicago, Detroit, Saint Paul and Minneapolis and by the end of 2020, the technology was available in ten cities nationwide.
The operator launched its 5G mobile services in selected areas of Chicago and Minneapolis in April 2019 using millimetre-wave spectrum. As of September 2020, the 5G mobile network was available in about 35 cities across the country and in December 2020 in 61. In October 2020, the company switched on its 5G network utilizing Dynamic Spectrum Sharing (DSS) technology, which allows 5G to run simultaneously on the same spectrum band as 4G. Verizon total footprint increased to 230 million people and covered 2,700 towns and cities.
AT&T
The company launched its ‘5G E’ mobile services in certain parts of selected cities in December 2018, using the 39 GHz frequency range. In April 2020, the company had rollout out its 5G network in the 850 MHz band in over 190 markets, covering about 120 million people. AT&T’s faster mm-wave network branded ‘5G+’ was launched for consumer access in March 2020, offering coverage in parts of 35 cities.
In late July 2020, AT&T announced that its 5G network using the 850 MHz band was available to 205 million consumers across the country. By November 2020, AT&T’s 5G network reached more than 225 million people in about ‘14,000 cities and towns across the U.S.’.
T-Mobile USA
In July 2019, T-Mobile USA pre-launched its 5G services in selected parts of six US cities (Atlanta, Cleveland, New York City, Los Angeles, Dallas, and Las Vegas) using the 28 GHz band.
In December 2019 T-Mobile switched on its 5G network using the 600 MHz frequency band. The deployment covered more than 200 million people and more than 5 000 cities and towns across the country. In January 2021, the operator announced its 5G network covered 280 million people, equivalent to more than 84% of the population. It should however be noted that data rates available with the 600 MHz spectrum alone is lower than the data rates provided by 4G services.
In late September 2020, T-Mobile US covered a total of 210 towns and cities using its 2.5 GHz band, the former Sprint spectrum. In November 2020, the operator communicated it had nearly double the number of locations with access to 2.5 GHz 5G connectivity, about 400, and that it planned to cover 100 million people by the end of 2020.
T-Mobile partnered with Cisco and Nokia to build its 5G core and Ericsson and Nokia for its 5G radio infrastructure.
T-Mobile USA and Sprint Merger
Sprint and T-Mobile officially merged into one company in April 2020. T-Mobile started to expand its network with spectrum re-farmed from Sprint in the 2.5 GHz band and opened nationwide 5G access for Sprint customers in the 600 MHz and mm-wave bands.
Sprint
Sprint had launched 5G services in May 2019 in three cities (Atlanta, Dallas Fort Worth, and Kansas City). In July 2019, it extended services to Chicago and in September 2019 to selected parts of Los Angeles, New York City, Phoenix and Washington DC. The Sprint 5G Non-Standalone network in the 2.5 GHz band was using massive 128-antenna MIMO equipment to be able to operate 4G at the same time.
8. Other countries
Bahrain
Batelco and STC announced that they had launched 5G services in June 2019. Batelco announced in October 2020 that its 5G network now covers 95% of the Kingdom’s population across all four governorates. In January 2020, STC’s 5G network was expanded to cover 50% of Bahrain’s territory.
Brazil
Telefonica
In July 2020, Telefonica launched its 5G network in selected parts of eight state capitals, namely: Sao Paulo, Salvador, Brasilia, Rio de Janeiro, Porto Alegre, Goiania, Curitiba, and Belo Horizonte. Rival Claro also launched 5G services in selected zones of in Sao Paulo and Rio de Janeiro in July 2020.
Claro
Claro launched its 5G network in July 2020 using a combination of 700 MHz, 1800 MHz and 2.5 GHz spectrum in areas in Sao Paulo and Rio de Janeiro. The operator announced plans to expand its 5G service in 12 additional cities before the end of 2020.
Canada
Rogers Communications
The operator started offering 5G services in March 2020 in parts of Vancouver, Toronto, Ottawa, and Montreal using equipment from Ericsson. In October 2020, the company announced the expansion of its 5G network to a total of 130 towns and cities. Rogers also disclosed that it added 600 MHz and AWS (1700 MHz) band frequencies to its original 2.5 GHz 5G commercial spectrum, having switched on Dynamic Spectrum Sharing (DSS) technology in a number of its new and existing 5G locations.
In December 2020 Rogers announced that it was starting to roll out Canada’s first 5G standalone (SA) core network, in partnership with Ericsson, initially to serve Montreal, Ottawa, Toronto and Vancouver, aiming to support future devices and chipsets as they become available.
Bell Canada
Bell started the construction of its 5G network in February 2020, using equipment from Finnish vendor Nokia. The carrier also selected Ericsson 5G Radio Access Network (RAN) technology to support its nationwide 5G mobile and fixed wireless access deployment. The operator launched commercial 5G services in Montreal, The Greater Toronto Area, Calgary, Edmonton, and Vancouver. In February 2021, the operator reported that the 5G network was available in more than 150 centres (cities and smaller communities) covering 24% of the Canadian population. Bell is targeting 5G population coverage of roughly 50% by end-2021.
Telus
The third largest operator by mobile subscribers, Telus, announced in June 2020, the selection of European vendors Ericsson and Nokia to build its 5G network. In June 2020, the operator announced the roll-out of its 5G network in Vancouver, Montreal, Calgary, Edmonton, and the Greater Toronto Area. The company planned to continue to expand to an additional 26 markets across Canada throughout the remainder of 2020. As of February 2021, Telus’ 5G presence reached over 50 towns and cities across the country. The mobile operator also revealed that it selected South Korea’s Samsung as a network infrastructure partner to provide ‘transformational 5G mobile services’.
Hong Kong
HKT, Hutchison 3 and China Mobile Hong Kong (CMHK) launched 5G services on April 1, 2020. CMHK announced its 5G network covers over 90% of the main areas of Hong Kong Island. HKT said coverage will initially reach 11 of the territory’s 18 districts.
India
The Indian government is strongly backing 5G deployment, but 5G is still in the early stages of reflection. The Department of Telecom (DoT) is harmonizing spectrum in the 3.3-3.6 GHz and 26 GHz bands, along with the 71-76 GHz, the 81-86 GHz and the 57-64 GHz frequency ranges as 5G candidate bands. A reasonable target for 5G launch is 2022.
Israel
Pelephone announced the launch of its commercial 5G services in 150 locations in October 2020, including Tel Aviv, Haifa, Ra’anana, Dimona and Kiryat Shmona.
Kuwait
All the three MNOs in Kuwait launched 5G services in July 2019.
New Zealand
Vodafone New Zealand launched 5G services in parts of Auckland, Wellington, Christchurch, and Queenstown in December 2019. In March 2021, Vodafone New Zealand announced 5G mobile and broadband services were available in parts of Tauranga.
Spark launched 5G service in July 2020 in Palmerston North and promised four more locations will be added before the end of the year. By March 2021, 5G services were available in six cities.
Oman
Omantel launched 5G home services in December 2019. The network covered parts of about 17 cities and towns. The operator launched 5G mobile services in February 2021 in parts of over 7 locations. Ooredoo followed and launch 5G services in May 2020 in over 6 cities and towns.
Philippines
Globe Telecom launched 5G FWA services in June 2019 in parts of Bulacan, Cavite City, and Rizal. PLDT launched its 5G mobile network in the main business districts of Metropolitan Manila in late July 2020. Smart Communications launched its 5G network in September 2020.
Qatar
Ooredoo in Qatar claimed in May 2018 to be the first world player to launch 5G nationally with 50 sites registered late in July 2018. Ooredoo seemed to be providing 5G wTTH (wireless To The Home) services in the 3.5 GHz spectrum range domestically with very few compatible devices available. In July 2019, the operator launched its 5G mobile network and by September 2020 the coverage reached ‘more than 90% of populated areas in Qatar.
Vodafone Qatar launched 5G services in August 2019.
Saudi Arabia
The SA Kingdom set up a national 5G task force to prepare the foundations for a large-scale 5G rollout before the end of 2019.
Zain and STC launched 5G services in June 2019. By February 2021, Zain’s 5G network covered 44 cities across the country and STC 5G services were available in 22 cities.
Singapore
M1 announced that it switched on its 5G non-standalone network in Singapore in September 2020. Coverage was available in Singapore’s central business district, and other selected areas. The operator announced plans to extend coverage to the rest of the country’s key urban areas/towns by the end-2020.
South Africa
In May 2020, Vodacom turned on 5G in Johannesburg, Pretoria, and Cape Town. Wider coverage is expected throughout the year. MTN rolled out 5G services in areas of Bloemfontein, Cape Town, Edenvale, Johannesburg, Hopetown, Queenstown, Port Elizabeth, Port Alfred in July 2020. Rain launched 5G services in areas of Cape Town, Johannesburg & Tshwane in July 2020.
Thailand
In March 2020, Advanced Info Service (AIS) launched 5G services on the 2.6 GHz range it acquired from auction concluded the same month. By February 2021, the network covered 200 locations and had 5,400 base stations.
True launched commercial 5G services were launched in March 2020 via 400 BTS in the 2.6 GHz band, while the 700 MHz band was enabled in January 2021 and 5G in the 26 GHz range was added in February 2021. By March 2021, True offered 5G connectivity in 355 locations in all 77 provinces.
DTAC commenced commercial 5G services in the 700 MHz band in December 2020. As of February 2021, 5G is offered in six provinces.
Taiwan
Taiwan Mobile launched 5G services in July 2020 in major cities via 2,000 base stations. Taiwan Star launched its commercial 5G services in August 2020. 5G coverage in Taiwan’s major metropolitan areas has reached 50% and is expected to top 80% by the end of 2020. APT launch 5G commercial services in October 2020 in ‘parts of densely populated areas.
UAE
Du announced the rollout in 2018 of a limited 5G network. In June 2019, its 5G services using the 3.5 GHz and 2.6 GHz bands were launched and by February 2021, it had 200 base stations in main urban areas. Etisalat’s planned to roll out 5G commercial fixed devices in September 2018.
In May 2019, 5G mobile services were available and by February 2021, the network was available in main urban areas.
Uruguay
Antel launched a commercial 5G network in April 2019, in Manantiales, though limited in reach.